Imagine: your skin problem is an unwelcome guest, and laser technology is two distinctly different eviction experts. One is the Flash Pico Laser, which uses picosecond level ultra fast pulses to accurately strike color spots and tattoos; The other is geologist Nd: YAG Laser, who specializes in stubborn birthmarks and red blood streaks with deep penetrating power. They may seem like Warriors of Light, but their combat strategies and battlefields are vastly different – one excels in surface lightning warfare, while the other is proficient in genuine leather endurance warfare. So the question is: Which expert should you invite to solve your skin problems?
Don’t rush to answer! Pico Laser is like a delicate artist, almost painless during treatment, and can be done during lunch break, suitable for urbanites who believe that time is money; Nd: YAG Laser, on the other hand, is more like a calm surgeon who may require a little anesthesia, but can penetrate deep into the skin’s basement to clear long-standing ailments. Interestingly, the former can also secretly stimulate collagen regeneration, while the latter is more friendly to dark skinned people. The key to victory in this Marvel showdown in the laser industry is actually hidden in your skin problems-now, are you ready to decode their secrets?
An Comprehensive Understanding of the Working Principles Pico Laser and Nd:YAG Laser
By utilizing the explosive effect and selective absorption principle of laser, high-energy laser pulses are applied to pigment tissues (melanin, tattoo pigments, permanent tattoo agents, dust particles) and absorbed by them. The pigment tissues are rapidly expanded after laser shock and heating. Due to the laser pulse being much lower than the thermal relaxation time of melanin structure and tattoos in the body, the pigment tissues absorb laser energy and generate mechanical oscillation waves to crush them. The ruptured pigment particles are then engulfed by the body’s metabolism and macrophages, and eliminated from the body, ultimately removing the pigment. At the same time, the laser beam can effectively penetrate the dermis layer, promote tissue activity, accelerate collagen cell regeneration, thereby achieving wrinkle removal, whitening, skin rejuvenation, and improving skin quality. Due to the principle of selective thermal absorption of lasers, the optimal absorption wavelengths for various pigments are different. However, the absorption of 1064nm and 532nm lasers output by other lasers in the human body is extremely small. Therefore, this device can effectively remove diseased pigments and vascular tissues without damaging surrounding tissues.

By utilizing the principle of selective photothermal action of lasers and the explosive action principle of Q-switched lasers, precise doses of specific wavelengths of energy can be directed towards a specific structural chromophore: exogenous pigment particles and endogenous melanocytes in a very short period of time. After absorbing the laser, the pigment undergoes a sudden explosion due to heat, being shattered into smaller particles. The fragmented particles are then engulfed by macrophages through metabolism and enter the lymphatic circulation with macrophages, resulting in the pigment being excreted from the body. The pigment gradually fades, and after periodic treatment, the pigment finally disappears, thus achieving the goal of treatment. The principle of laser selective photothermal therapy is currently recognized as the best non-invasive method for treating pigmentary skin lesions.

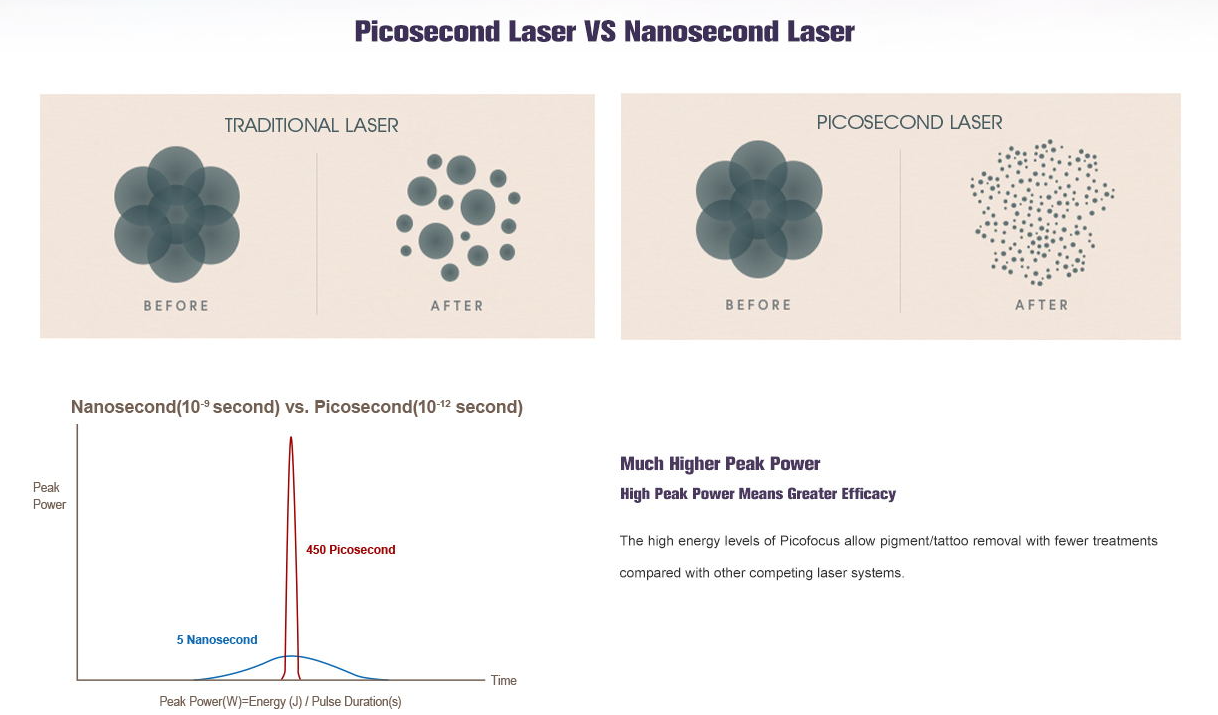
Exploring the Strengths: Pico Laser vs. Nd:YAG Laser
Pico Laser
Picoseconds significantly reduce damage to surrounding tissues, shorten the recovery period after treatment, and lower the risk of pigmentation. Traditional Q-switched lasers mainly utilize photothermal effects, which inevitably damage surrounding normal tissues while crushing pigment particles. However, ultra picosecond lasers, due to their rapid impact, greatly reduce the damage to surrounding normal tissues while crushing pigment particles, thereby reducing the probability of color fading.
The effect of a single treatment is more significant, and the number of treatments required for the entire course of treatment is reduced. Picoseconds can reduce the number of treatments and greatly shorten the treatment time by crushing pigment particles smaller.
The treatment comfort is very high and the incidence of adverse reactions is low. Traditional laser has a strong sense of pain, and if anesthesia is applied, it will affect the effectiveness. Picosecond therapy is the most comfortable among all laser treatments, although it may cause some pain, it is completely tolerable and there is basically no strong pain sensation.
Nd:YAG Laser
- switched laser adopts a non ablative treatment method, which will not damage skin tissue during the treatment process, is safe and reliable, and will not cause adverse consequences or complications. It utilizes the principle of selective photothermal action to quickly decompose melanin, efficiently fade pigmentation and brighten skin tone.
At the same time, the pigments in the skin tissue can instantly absorb the high energy of specific wavelength lasers, making the treatment process rapid and effective. This treatment method is very convenient, can be treated as needed without a recovery period, and does not affect daily life, study, and work at all. Due to the fact that the treatment process does not require injection anesthesia, it not only avoids trauma, but also ensures no side effects or sequelae, providing a safe and efficient solution for skin problems for beauty seekers.

Significant Differences in Treatment Indications and Clinical Outcomes
Pico laser and Nd: YAG laser each have their own advantages in terms of treatment scope. Pico laser, with its picosecond ultra short pulses, is highly effective in removing pigmentation problems in the epidermal layer (such as freckles, sunspots, and melasma) and stubborn tattoos, especially adept at handling pigmentation of small particles. Nd: YAG laser, with its longer wavelength of 1064nm, penetrates deeper and is more suitable for dermal problems (such as Ota nevi, brown blue nevi in the zygomatic region) and vascular lesions (such as spider nevi, red blood streaks). At the same time, it is safer for hair removal treatment in dark skinned individuals. The two types of lasers complement each other in terms of treatment depth and target tissue selection, and are often used in combination according to the lesion level in clinical practice.
The Clear Difference Between the Treatment Process and Experience
From the patient experience, Pico laser treatment causes milder pain, which can usually be tolerated with only surface cold spraying or application of anesthesia cream. After surgery, there is only a brief redness that can disappear within 1-2 days, making it suitable for busy workers. During Nd: YAG laser treatment, there may be a significant warm and stinging sensation. Some deep treatments may require local anesthesia, and temporary redness or slight scabbing may occur after surgery, with a recovery period of about 3-5 days. In addition, Pico laser has a shorter single treatment time (usually 15-20 minutes), while Nd: YAG laser may take more than 30 minutes for a single treatment due to the need for layered treatment, and the interval between treatment courses is relatively longer.
Comparison of Long-term Effects and Duration
In terms of long-term efficacy, picosecond laser usually only requires 1-2 treatments to effectively remove epidermal pigments, and the recurrence rate is low (especially when combined with sunscreen), but more treatment courses are needed for deep pigments. In contrast, Nd: YAG laser requires 3-5 treatments to significantly improve dermal pigmentation lesions, but once cleared, there is almost no recurrence. It is worth noting that picosecond laser can simultaneously promote collagen regeneration and has a cumulative skin rejuvenation effect; The therapeutic effect of Nd: YAG laser on vascular lesions (such as telangiectasia) is more long-lasting, and a single treatment can usually last for more than 1 year. The difference in the duration of effectiveness maintenance between the two directly affects the frequency of treatment and the choice of long-term care plan for patients.
