In laser beauty field, picosecond laser symbolize a new era. Compared to traditional nanosecond laser, picosecond pulse duration is reduced by thousand times. It means the energy can be released in a shorter time to generate stronger photomechanical effect and smash the pigmented particles more precisely. However, technology advancement is only half the battle. The true clinical effect and safety are decided by another key factor-wavelengths selection.
Different wavelengths can selectively absorb targeted tissue. This directly decide the effectiveness, safety and application range. Here, we will explore how do picosecond five key wavelengths(1064nm, 755nm, 532nm, 585nm, 650nm) work to do treatment more safety and efficient.
1. Scientific Base of Wavelengths Selection: Why Is This the Picosecond Core Advantage
1.1 Further Application of Selective Photothermal Decomposition Theory
Selective photothermal decomposition demands the laser wavelength can be absorbed by target chromophore. Picosecond laser has advanced this theory. After the target tissue absorbed the energy, ultra-short pulse will immediately generate photomechanical blast but not thermal diffusion.
1.2 Differences in the Absorption Characteristics of Skin Pigments
The main pigments such as melanin, hemoglobin and exogenous tattoo ink are different in absorbing lasers of different wavelengths. This difference forms the basis for wavelength-selective therapy.
1.3 Balance Between Penetration Depth and Safety
The wavelength directly affects the penetration depth of laser in the skin. Shorter wavelengths (such as 532nm) mainly act on the epidermis and superficial pigments, while longer wavelengths (such as 1064nm) can safely reach the dermis layer. Picosecond laser can precisely control the level of action and avoid unnecessary tissue damage through wavelength selection.
2. Detailed Explanation of the Characteristics and Clinical Applications of the Five Key Wavelengths
2.1 1064nm wavelength: the Cornerstone Solution for Deep Pigment Problems
The 1064nm near-infrared wavelength is one of the core wavelengths of picosecond systems, which has the dual advantages of deep penetration and high safety. Melanin has good absorption at 1064nm, while hemoglobin absorption is extremely low, making it an ideal choice for treating deep pigment lesions.
- Main Clinical Applications
Deep level skin pigmentation lesions such as Ota nevus and brown blue nevus on the zygomatic region
Removal of Black and Blue Black Tattoos
Skin rejuvenation treatment stimulates deep collagen regeneration
Preferred wavelength for Asian skin pigmentation issues (high melanin absorption, low risk of epidermal damage)
2.2 532nm Wavelength: Solution to the Problem of Epidermal Pigments and Redness
The 532nm green light wavelength is located between the absorption peaks of hemoglobin and melanin, and has good targeting for superficial pigments and red targets.
- Main Clinical Applications
Skin pigmentation diseases such as freckles, sunspots, coffee spots, etc
Removal of Red and Orange Tattoos and Eyebrow Tattoos
Treatment of superficial capillary dilation
Caution should be exercised when used for darker skin tones to avoid the risk of hypopigmentation
2.3 755nm Wavelength: the Gold Standard for Melanin and Blue-green Tattoos
The 755nm emerald green gemstone laser wavelength is considered the “gold standard” in the industry for treating melanin problems and blue-green tattoos, achieving an excellent balance between melanin absorption and low hemoglobin absorption.
- Main Clinical Applications
Treat brown and melanocytic lesions (such as sunspots and seborrheic keratosis)
Remove green and blue tattoo pigments (with high absorption peak matching)
Hair removal treatment (targeting hair follicle melanin)
Overall high safety, suitable for various skin types
2.4 585nm Wavelength: For Vascular Lesions and Skin Rejuvenation
The 585nm yellow light wavelength is located near the hemoglobin absorption peak, exhibiting high selectivity towards microvessels while retaining moderate melanin absorption capacity.
- Main Clinical Applications
Vascular lesions such as fresh red nevus and hemangioma
Improvement of redness and acne scars after inflammation
Skin rejuvenation treatment improves skin texture and fine lines
The auxiliary role in the comprehensive treatment of melasma
2.5 650nm Wavelength: A Supplementary Weapon for Special Color Tattoos and Stubborn Pigments
The 650nm red light wavelength serves as an important supplement to multi wavelength systems, providing solutions for specific color and stubborn pigment problems.
- Main Clinical Applications
Removal of Purple, Blue, and Partial Green Tattoos
Supplementary treatment for pigment problems resistant to traditional laser therapy
Combined with other wavelengths to enhance the overall therapeutic effect
3. Multi Wavelength Collaboration: A Safety Guarantee System for Personalized Treatment
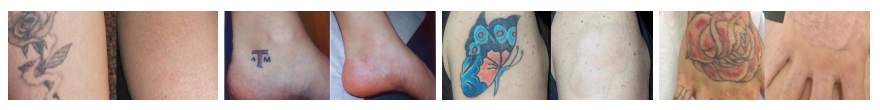
3.1 Comprehensive Solution to Multi-level Pigment Problems
Facial pigmentation problems often present multi-level and multi type characteristics. For example, melasma may exist in epidermal, dermal, and mixed types simultaneously, requiring precise combinations of different wavelengths. 1064nm can handle deep dermal pigments, 532nm targets epidermal pigments, and 585nm improves accompanying vascular problems, forming a three-dimensional treatment plan.
3.2 Expansion of Security Boundaries: Comprehensive Consideration from Skin Color to Treatment Depth
The multi wavelength system enables doctors to select the safest wavelength based on the patient’s skin color, pigmentation depth, and type.
Darker skin tone: Priority should be given to wavelengths with relatively low melanin absorption and deep penetration, such as 1064nm and 755nm
Sensitive skin: 585nm isothermal and wavelength can be used to reduce the risk of inflammatory reactions
Complex lesions: treated in stages with multiple wavelengths to avoid excessive stimulation during a single treatment
3.3 Intelligent Optimization of Treatment Parameters: Precise Adjustment with Wavelength As the Core
Modern picosecond devices use wavelength as the core variable, combined with parameters such as energy density and lattice mode to form a multidimensional regulation system. This wavelength oriented parameter optimization enables treatment to truly achieve “personalized customization” rather than a “one size fits all” approach.
4. Safe and Effective Dual Guarantee: Beyond the Wavelength Itself
Emphasizing the fundamental role of wavelength does not mean it is the only factor. Safe and effective treatment is a systematic engineering.
4.1 Accurate Parameter Settings
The energy density, spot size, pulse frequency, etc. need to be matched with the wavelength and adjusted according to individual reactions.
4.2 Advanced Laser Technology
Picosecond level pulse width, lattice focusing lens and other technologies ensure precise energy transfer.
4.3 Professional Operators
The experience of doctors is crucial, as they are responsible for diagnosis, wavelength selection, parameter setting, and postoperative guidance.
4.4 Pre and Post Operative Preparation
Comprehensive preoperative and postoperative care, including skin condition assessment, sun protection, moisturizing repair, etc., is an important link in achieving long-lasting therapeutic effects and avoiding complications.
4.5 Wavelength Selection
Wavelength selection is the core decision-making point of this system engineering, which guides the direction of treatment. The correct direction, coupled with excellent technology and operation, can ultimately reach a safe and effective endpoint.
FAQ
Q1: Is it better for picosecond lasers to have more wavelengths?
A: It’s not simply “more is better”. The key depends on whether the wavelength integrated by the device is accurate, efficient, and can cover common clinical target tissues. The core and validated wavelength combinations (as mentioned in the article) are sufficient to address the vast majority of indications. More importantly, doctors have the ability to select the most suitable wavelength based on the problem.
Q2: Why do we need different wavelengths to treat different spots?
A: Because the type, depth, and pigment composition of the spots are different. For example, epidermal freckles are suitable for 532nm, dermal Ota nevi require 1064nm, and mixed yellow brown spots require 755nm, which can accurately target melanin and have minimal impact on blood vessels. Choosing a matching wavelength is necessary to achieve optimal results and minimize risks.
Q3: What are the consequences of using the wrong wavelength for picosecond lasers?
A: May lead to poor therapeutic effect, energy absorption by non target tissues, increased risk of skin burns, pigmentation or hypopigmentation, scarring, etc. For example, using wavelengths that are mainly absorbed by hemoglobin to extract melanin may have poor results and can easily damage blood vessels.
Q5: How do I know which wavelength of treatment is suitable for me?
A: This must be decided by a professional doctor after a face-to-face consultation. Doctors will evaluate pigment levels and types using tools such as dermatoscopy and Wood lamps, and develop personalized wavelength and treatment plans based on your skin condition and medical history. Do not make judgments on your own.
