Pigmentation issues have always been a stubborn problem for beauty enthusiasts, whether it is superficial freckles or deep Ota moles. These unwanted pigmentation deposits not only affect aesthetics, but may also have profound effects on patients’ psychological state and quality of life. With the development of laser technology, Q-switched Nd: YAG laser has demonstrated excellent clinical value in the treatment of pigmentary diseases due to its unique 1064nm wavelength characteristics. This laser system is based on the principle of selective photothermal action, which can accurately target melanin particles at different depths, achieve targeted treatment effects, and maximize the protection of surrounding normal tissues, bringing breakthrough progress to the treatment of pigmentary skin problems.
Clinical studies have shown that YAG lasers have outstanding advantages in the treatment of pigmented lesions. Its long wavelength of 1064nm can accurately act on pigmented lesions deep in the dermis (such as nevus of Ota), while the short wavelength adjusted by special technology can specifically treat epidermal pigment deposition. It is worth noting that compared with traditional laser equipment, YAG lasers significantly reduce the risk of pigmentation in the treatment of Asians and have a higher safety factor. With the application of picosecond technology, the new generation of YAG lasers has achieved a breakthrough improvement in efficacy, providing a safer and more reliable treatment option for beauty lovers who pursue perfect skin.
YAG laser Working Mechanism: In-depth Analysis of the Principle of Selective Photothermal Decomposition
The scientific principle of YAG laser treatment for pigmentary diseases is based on the theory of selective photothermal decomposition. The specific wavelength of 1064nm output by the laser system can be selectively absorbed by melanin particles, while the surrounding tissues absorb very little of it. When a nanosecond pulse width laser is applied to the target tissue, melanin absorbs light energy and undergoes instantaneous gasification, producing strong optomechanical effects that cause physical fragmentation of pigment particles, which are then cleared through the skin metabolic pathway. The core of this process lies in precise control of the thermal relaxation time – the duration of the laser pulse must be shorter than the thermal diffusion time of the target tissue to ensure that heat is confined to the target area and avoid thermal damage to surrounding tissues.
From a molecular perspective, the efficacy of YAG laser depends on the efficiency of light pigment interaction. 1064nm wavelength can penetrate deep into the dermis (3-5mm), mainly targeting melanin in the dermis (such as Ota nevus); The 532nm wavelength is more strongly absorbed by epidermal melanin and is suitable for superficial pigments. Clinical observations have found that peak power density is the threshold for inducing luminescent mechanical effects.
Clinical Indications and Therapeutic Advantages of YAG Laser In the Treatment of Pigmentation
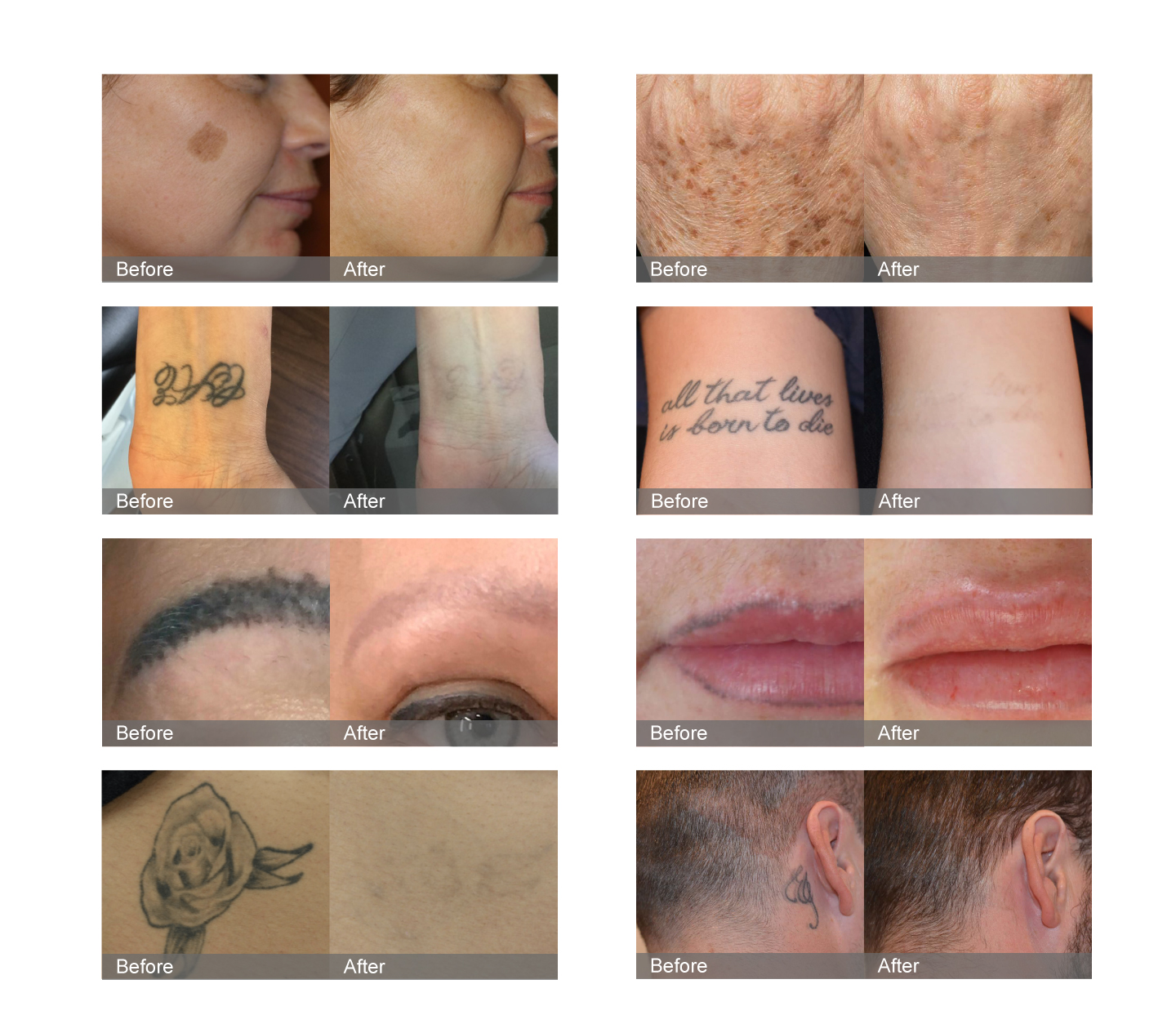
YAG laser, with its unique dual wavelength system of 1064nm and 532nm, has demonstrated a wide range of clinical indications in the treatment of pigmentary diseases. For dermal pigmentation lesions such as Ota’s nevus, Ito’s nevus, Mongolian spot, and cheekbone brown blue nevus, a wavelength of 1064nm can effectively penetrate the dermis layer and selectively destroy melanin particles. The 532nm wavelength is more suitable for epidermal pigment lesions, including coffee spots, freckles, seborrheic keratosis, sunspots, and various pigmented nevi. In the treatment of mixed pigmentation diseases such as melasma, YAG laser can achieve layered treatment through precise parameter regulation. In addition, it also performs well in removing exogenous pigments (tattoos, eyebrow tattoos, etc.).
In addition to pigment therapy, YAG laser can also stimulate collagen regeneration through photothermal effects, achieving multiple effects such as skin rejuvenation, pore contraction, acne reduction, and even skin tone. It has important application value in the field of skin rejuvenation. Compared to traditional lasers, YAG laser treatment is safer and significantly reduces the incidence of postoperative pigmentation, especially suitable for the skin characteristics of Asian populations.
Two Treatment Methods of the YAG Laser
Invasive treatment
Advantages: The effect of removing pigments in a single session is better, shortening the treatment period.
Disadvantages: Due to excessive local energy on the skin, it is easy to cause thermal damage, with risks of scarring, darkening, and blackening. After treatment, there may be bleeding, resulting in low customer acceptance and poor experience.
Non-invasive treatment
Advantages: Due to the absence of skin breaking, the customer acceptance is high and the therapeutic effect can be guaranteed. The heat damage is low, and the risk of scars, darkening, and blackening is eliminated.
Disadvantages: The effect of removing pigmentation in a single session is not as good as that of transdermal treatment, and the treatment period is slightly longer compared to transdermal treatment.
Precise Operation Process of YAG Laser Treatment for Pigmentation
YAG laser treatment for pigmentary diseases follows standardized clinical procedures to ensure safety and effectiveness. Professional skin assessment is required before treatment, including pigment type diagnosis (dermal, epidermal, or mixed), skin phototype determination, and contraindication screening. During treatment, doctors will select wavelengths of 1064nm or 532nm based on the characteristics of the lesion, and accurately adjust the energy density, spot size, and pulse width. Immediately cool the skin after surgery to reduce inflammatory reactions, and cooperate with medical repair products. The treatment interval is usually 4-8 weeks, and strict sun protection is necessary to avoid pigmentation. The full process digital recording can optimize personalized treatment plans.
YAG Laser Standardized Operation Specifications and Clinical Considerations
Before Operation
Communicate fully with customers, understand their needs, physical condition (whether they have injections, use skincare products containing hormones, recent exposure to sunlight), take photos, and fill in customer information files
Check if the instrument is working properly and clean the lenses before treatment
Explain your feelings during treatment
In Operation
Wear goggles. The laser output port should never be aimed at human eyes.
The treatment handle should be perpendicular to the skin, and the same position operation cannot be repeated more than 3 times.
When stopping treatment, first release the foot pedal and then remove the treatment head.
Treat while soothing, constantly observe the customer’s skin reactions, and adjust treatment parameters in a timely manner.
After Operation
Apply repair products to promptly remove redness and repair
Explain the precautions after treatment and schedule the next treatment time.
Turn off the instrument and record the customer’s usage parameters
Analysis of People Who are Contraindicated in YAG Laser Treatment
YAG laser treatment has clear contraindications and strict screening of suitable populations is required. Absolute contraindications include: pregnant women, patients with photosensitive diseases, patients with total gold wire implantation, and patients with serious heart disease, hypertension, diabetes and other systemic diseases. Relative contraindications require careful evaluation: Skin with a recent (within two weeks) history of sun exposure should be temporarily treated; It is recommended to discontinue the use of hormone based drugs or highly effective skincare products before seeking treatment. When the skin is in a sensitive period or there are active wounds, eczema, urticaria and other lesions, the affected area should be avoided; Facial injection filling area (silicone permanently prohibited, other fillers must be at least 3 months old). People with scar constitution need to be fully informed of the risks. In addition, a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s medication history, skin condition, and previous cosmetic treatment history is required before treatment to ensure treatment safety.
Summary:The principle and clinical application of YAG laser in treating pigment problems.