Prevention and Management of Adverse Reactions to IPL Therapy
IPL technology has become a universal treatment method in the dermatology and medical aesthetic fields because of its non-invasivness, multifunctions and wide application.
In skin reconstruction, IPL clinical treatment can be divided into I type skin rejuvenation and II type rejuvenation. As for the clinical treatment classification, it can be divided into pigmented lesion treatment, vascular treatment and hair removal treatment. However, the clinical studies show that it also does goods to whiten skin, improve the dull skin and treat acne, freckles and melanosis of the skin.
As it is widely applied day by day, the management challenges of adverse reactions that clinical doctors are facing become more apparent. Now, let’s explore the adverse reactions and its scientific prevention measures to provide clinical treatment a more pragmatic and safer reference.
1. Common Adverse Reactions After IPL Treatment
The adverse reactions after IPL treatment can be divided into two categories: short-term reversible reactions and long-term complications, which clinical doctors need to accurately identify and classify for treatment.
1.1 Short Term Reversible Reactions (incidence>60%)
Redness and edema: often appear immediately after treatment, usually lasting for several hours to 48 hours, caused by vasodilation due to photothermal effects.
Burning and stinging sensation: About 80% of patients report mild to moderate burning sensation after treatment, which usually subsides on its own within 0.5-2 hours.
Dry and flaky skin: The photothermal effect temporarily damages the sebum membrane, leading to a temporary weakening of the barrier function, with an incidence rate of about 40%.
1.2 Mid Term Complications (2 weeks to 3 months)
Pigmentation (anti blackening): It is more common in exposed areas such as the zygomatic and temporal regions. People with dark skin (Fitzpatrick IV-V type) have a threefold increased risk and usually gradually subside within 3-6 months.
Hypopigmentation: rare but slow to recover, often caused by excessive energy or insufficient cooling.
Acne like rash: Photothermal activation of sebaceous glands, oily/mixed skin patients have a higher risk of treatment before and after menstruation.
1.3 Serious Complications (rare but cautious)
Blisters and burns: caused by improper parameter settings or cooling system failures, can progress to scars.
Infection: often caused by improper postoperative care leading to wound contamination.
Scar formation: common in patients with wound infection or scar constitution.
2. What Adverse Reactions Are IPL Treatment Easy to Cause
The occurrence of adverse reactions is by no means accidental and is closely related to three major factors.
2.1 Patient Factors
Skin color type: Patients with Fitzpatrick classification IV or above have a significantly increased risk of pigmentation.
Photogenic status: recent exposure to sunlight (within 2 weeks), taking photosensitive drugs (tetracyclines, isotretinoin, etc.).
Basic diseases: photosensitive diseases such as lupus erythematosus and polymorphous light rash, and diabetes affects wound healing.
2.2 Technical Factors
Improper parameter settings: High energy density is the primary cause of burns.
Equipment issues: Insufficient cooling of the treatment head, aging of the filter, and overlapping of light spots>20%.
Operation technique: The treatment head is not vertically attached to the skin, and the movement speed is uneven.
2.3 Postoperative Management Negligence
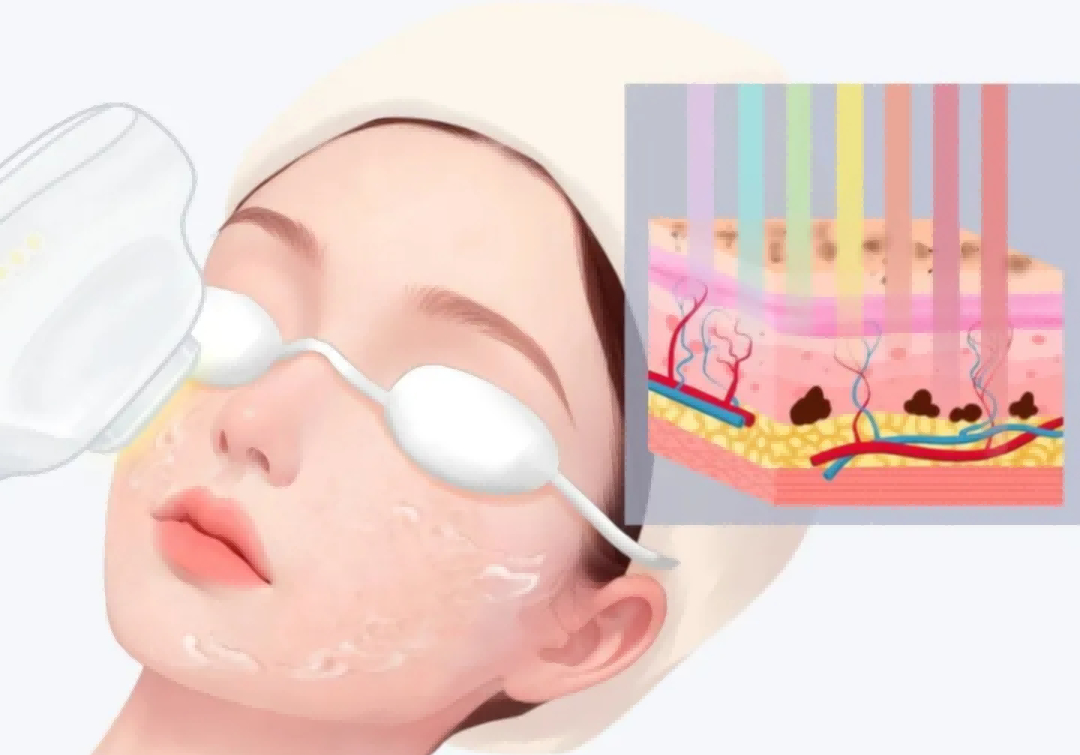
Lack of sun protection: Postoperative UV exposure is the main cause of pigmentation
Improper care: early use of irritating skincare products (alcohol, fruit acids).
High temperature exposure: Within one week after treatment, steam sauna and high-temperature yoga can accelerate the inflammatory response.
3. How to Prevent Complications
3.1 Fine Preoperative Evaluation (key first step)
Strict screening contraindications: pregnancy, photosensitive diseases, oral isotretinoin (to be discontinued for 3 months), recent exposure history.
Skin color classification+potential melasma detection: For patients with dark skin, it is recommended to undergo 4-6 weeks of whitening pre-treatment (hydroquinone cream/tranexamic acid) first.
Pretreatment of sensitive muscles: Apply medical moisturizing facial mask 30 minutes before operation to improve skin tolerance.
Parameter Adjustment Strategies for Different Skin Types
| Skin Type | High-risk Side Effect | Parameter Adjustment | Auxiliary Measures |
| Sensitive Skin | Persistent Erythema | Decrease 20% energy intensity and increase pulse width | Repair the barrier 2-4 weeks before treatment |
| Oil/Mixed Oil Skin | Acneiform Rash | Avoid operation before and after menstruation | Salicylic acid oil control after treatment |
| Pigment-active Skin | PIH | Choose long wavelength filter(≥590nm) | Combined with low concentration hydroquinone pretreatment |
| Dark Skin Tone | Permanent Pigment Change | Decrease 20% energy intensity, double pulse mode | Prolong the treatment interval to eight weeks |
3.2 Precise Parameter Setting (core technology)
Must do test spot:
Underneath the earlobe or mandibular angle, observe the endpoint reaction (ideal for slight redness), and wait for 5-8 minutes to confirm the actual reaction.
Dynamic cooling technology: Cool the entire process before, during, and after treatment, maintaining the epidermal temperature below 40 ℃ to prevent thermal damage.
3.3 Standardized Postoperative Care (efficacy guarantee)
Immediate treatment: after cleaning the cold gel, immediately use the mechanical type cold compress (15-30 minutes)
For those with obvious erythema: Apply weak acting hormone ointment (0.1% mometasone furoate) locally for 3 days.
3.4 Two Principles of Home Care
Gentle cleaning: Wash your face with cold water only 72 hours after surgery to avoid friction.
Ultimate sun protection: Hard sun protection (mask+hat) for 3 days after surgery, followed by the addition of SPF50+physical sunscreen 3 days later.
Behavioral taboos: Avoid high temperature environments (sauna, hot yoga), vigorous exercise, and alcoholic skincare products within 72 hours.
4. How to Handle the Adverse Reactions
4.1 Mild Redness and Swelling: 1-2 Hours After Treatment
Reference plan: Apply cold compress until there is no burning sensation in the treatment area, or rinse the treatment area with cold water.
4.2 Moderate redness and swelling: The Skin Remains Red and Swollen for 1-2 Days After Treatment.
Causes: photosensitive reaction, inadequate postoperative care, excessive energy, etc.
Solution: Apply cold compress to cool down. For those with severe edema, a solution of 500m1 physiological saline, 400000 units of gentamicin, and 10mg dexamethasone can be prepared and placed in the refrigerator. Wet the solution with gauze or a facial cleanser.
4.3 Severe Redness, Swelling, and Blisters
1-2 weeks after treatment, skin edema does not subside, exudate may even ulcerate.
Causes: inadequate postoperative care, treatment of vascular diseases, excessive energy consumption, etc.
Solution: Small blisters should be allowed to absorb on their own, while large blisters should be treated with puncture and drainage to prevent infection, combined with growth factor sprays to promote healing, following the principle of spraying first and then applying. External application of gel drugs, cotton swab application, 3 to 4 times a day. If any exudate is discharged, it should be cleaned promptly with a cotton swab or gauze to avoid the formation of thick dry scabs. Do not manually remove the scabs and let them fall off naturally.
4.4 Pigmentation
After scab shedding, large areas of darkening or worsening pigmentation appear.
Causes: Failure to rule out contraindications, sun exposure before and after treatment, excessive energy, etc.
Solution: Strict sun protection. Low energy mild light modulation therapy is performed using VC, VE or hydroquinone cream, tranexamic acid moisturizing antioxidant, fruit acid and other treatments, beauty therapy (microneedle, water light needle, nano crystal), physical introduction, Q-switched Nd: YAG1064nm laser, ruby laser, etc.
4.5 Pigmentation Loss
The skin shows a decrease or loss of pigmentation in the local area after scab shedding.
Causes: Suffering from pigment regeneration disorders, high energy levels, etc.
Solution: Local medication such as Minbailin or tacrolimus can promote melanin synthesis. Illuminate 308 excimer light/laser. Use traditional Chinese medicine plum blossom needles and tap locally.
4.6 Facial Rash
The skin shows symptoms such as large papules, itching, redness, and swelling at the treatment site.
Causes: Incomplete facial cleansing, post acne inflammation, sensitive skin, and photosensitive reactions.
Solution: Water light deep cleaning can be used before treatment. Take orally 0.2g of hydroxychloroquine and 5mg of levocetirizine. Take one pill twice a day until the symptoms subside.
